Theoretical investigation on submicron particle penetration through circular tubes inside a porous medium |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China;2. School of Physics and Electronic-Electrical Engineering, Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China;1. College of Chemical Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266042, China;2. College of Chemical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300401, China;3. Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266101, China;1. School of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Newcastle, Callaghan 2308, Australia;2. School of Chemical Engineering, The University of Queensland, St Lucia 4072, Australia;3. Centre for Bulk Solids and Particulate Technologies, Newcastle Institute for Energy and Resources, The University of Newcastle, Callaghan 2308, Australia;1. Graduate School of Bio-Applications and Systems Engineering, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Nakacho, Koganei-shi, Tokyo 184-8588, Japan;2. Institute of Global Innovation Research, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Nakacho, Koganei-shi, Tokyo 184-8588, Japan;3. State Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering, Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, China;1. College of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China;2. Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Mine Mechanical Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China;3. School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China;4. School of Mechanical Engineering, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou 450045, China;1. Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, National Engineering Laboratory for MTO, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian 116023, China;2. State Key Laboratory of Heavy Oil Processing, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China |
| |
| Abstract: | 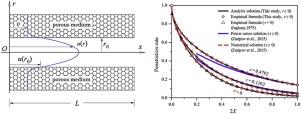
The analytical infinite series solution of submicron particle transport in a circular tube bounded by a porous wall, such as a pinhole, is determined under the slip velocity boundary condition, and the solution is verified by using the experimental data in the previous studies for the specific cases. The results show that particle penetration rate increases with the increase of the porous parameter, the axial pressure drop, and the pinhole radius, whereas it decreases with increasing the pinhole length. The penetration rate of nano-particles are more sensitive to the variation of these parameters. However, the differences between the penetrations of particles ranging from 0.3 μm to 1 μm are not evident because the diffusion becomes weak gradually in this size range. In addition, a further comparison is performed between the analytical solution and the existing studies, and approximate expressions are presented for accurate calculation of particle penetration rate through pinholes appearing in porous materials including filter devices and masks. |
| |
| Keywords: | Porous medium Penetration Submicron particle Circular tube Analytical solution |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

