Defects related emission and nanosecond optical power limiting in CuS quantum dots |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. School of Pure & Applied Physics, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam 686560, India;2. Light and Matter Physics Group, Raman Research Institute, C.V. Raman Avenue, Sadashivanagar, Bangalore 560080, India;1. Donbass State Engineering Academy, Kramatorsk 84313, Ukraine;2. Grupo de Materia Condensada UdeA, Instituto de Física, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Antioquia-UdeA, Calle 70 No. 52-21, Medellín, Colombia;3. Escuela de Ingeniería de Antioquia-EIA, Medellín, Colombia;4. Centro de Investigación en Ciencias, Instituto de Investigación en Ciencias Básicas y Aplicadas, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Av. Universidad 1001, CP 62209 Cuernavaca, Morelos, México;1. School of Electrical Engineering, Pusan National University, San 30, Jangjeong-Dong, Gumjeong-Ku, Busan 609 735, South Korea;2. Research Center For Dielectric & Advanced Mater Physics, Pusan National University, San 30, Jangjeong-Dong, Gumjeong-Ku, Busan 609 735, South Korea;1. School of Material Science and Nanotechnology, Jadavpur University, Kolkata 700032, India;2. Thin Film and NanoScience Laboratory, Department of Physics, Jadavpur University, Kolkata 700032, India;1. Department of Mathematics and Physics,Hunan Institute of Engineering, Xiangtan 411104, China;2. The Cooperative Innovation Center of Wind Power Equipment and Energy Conversion, Xiangtan 411104, China;3. College of Physics and Electronic, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;1. School of Physics and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, China;2. Institute of Fluid Physics, Chinese Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China |
| |
| Abstract: | 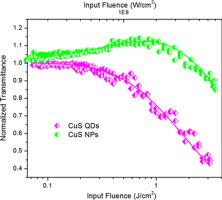
We report optical and nonlinear optical properties of CuS quantum dots and nanoparticles prepared through a nontoxic, green, one-pot synthesis method. The presence of surface states and defects in the quantum dots are evident from the luminescent behavior and enhanced nonlinear optical properties measured using the open aperture Z-scan, employing 5 ns laser pulses at 532 nm. The quantum dots exhibit large effective third order nonlinear optical coefficients with a relatively lower optical limiting threshold of 2.3 J cm−2, and the optical nonlinearity arises largely from absorption saturation and excited state absorption. Results suggest that these materials are potential candidates for designing efficient optical limiters with applications in laser safety devices. |
| |
| Keywords: | CuS quantum dots Emission Optical nonlinearity Surface states |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

