| 激光冲击修复后压力容器钢Q345R耐腐蚀及抗疲劳性能研究 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 张浩, 蒋磊, 岑志波, 张拔杨, 谢作然, 朱珏. 激光冲击修复后压力容器钢Q345R耐腐蚀及抗疲劳性能研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(10): 103101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0394 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 张浩 蒋磊 岑志波 张拔杨 谢作然 朱珏 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1. 宁波大学机械工程与力学学院,浙江 宁波 315211; 2. 宁波市特种设备检验研究院,浙江 宁波 315211; 3. 宁波计量测试研究院,浙江 宁波 315211 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金(11972203,11572162);宁波市自然科学基金(202003N4152) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 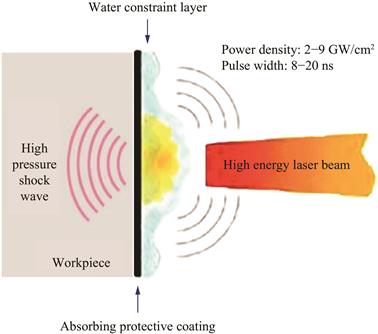
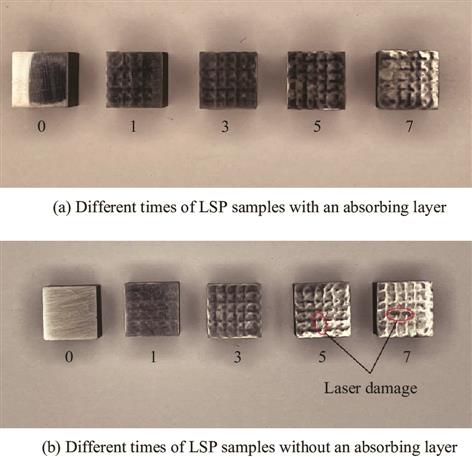
对激光冲击强化后的压力容器材料Q345R钢的耐腐蚀性能和抗疲劳性能进行研究。通过电化学实验,并结合扫描电子显微镜分析其耐腐蚀性。结果显示,有吸收层保护和无吸收层保护激光冲击后,相较于原试样,耐腐蚀性分别提升5.8倍和2.6倍;微观实验结果表明经过激光冲击后腐蚀试样表面裂纹明显少于未处理试样。
但随着冲击次数增加,耐腐蚀性有所下降。疲劳试验结果显示,相同应力条件下,腐蚀1和2 h的疲劳寿命相较于原试样降低36.8%和56.4%,经过一次或三次激光冲击后试件的疲劳寿命分别提升43.8%和198.2%,经XRD检测,激光冲击能在表面形成一定深度的残余压应力层并抑制裂纹扩展。
|
| 关 键 词: | 激光冲击强化 电化学腐蚀 极化曲线 疲劳寿命 微观形貌 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-09-22 |
| 修稿时间: | 2021-12-16 |
|
| 点击此处可从《爆炸与冲击》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《爆炸与冲击》下载全文 |
|



