|
|||||
|
|
A glassy carbon electrode modified with FeS nanosheets as a highly sensitive amperometric sensor for hydrogen peroxide |
|
| Authors: | Jiayi?Jin Wenqin?Wu Hui?Min |
| Institution: | 1.Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Advanced Organic Chemical Materials & Key Laboratory for the Synthesis and Application of Organic Functional Molecules, Ministry of Education & College of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering,Hubei University,Wuhan,People’s Republic of China;2.College of Chemistry and Materials Science,Hubei Engineering University,Xiaogan,People’s Republic of China;3.Hubei Key Laboratory of Pollutant Analysis & Reuse Technology,Huangshi,People’s Republic of China |
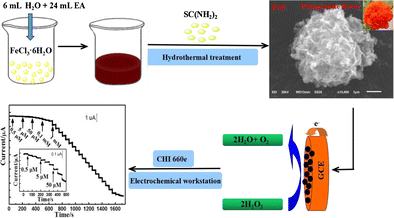
| Abstract: | Iron sulfides with different atomic ratios were synthesized by a hydrothermal method and used to modify a glassy carbon electrode. The various sulfides were compared to each other for their amperometric response to H2O2. It is found that FeS is the most adequate material. Operated in 0.1 M NaOH solution at 0.4 V (vs. Ag/AgCl), the sensor based on FeS displays a linear response that extends from 0.50 μM to 20.5 mM of H2O2, with a sensitivity of 36.4 μA mM?1 cm?2 and a detection limit of 0.15 μM (at an S/N ratio of 3). The sensor is selective, stable and reproducible. Graphical abstract Schematic of the synthesis of pomegranate flower-like FeS by a hydrothermal route using ferric chloride and thiourea (SC(NH2)2) as the precursors, and ethanolamine (EA) as the structure-guiding auxiliary agent. A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) modified with this material allows for amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide in 0.1 M NaOH solution with a 0.15 μM detection limit. |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 SpringerLink 等数据库收录! | |