Silylation of sodium silicate-based silica aerogel using trimethylethoxysilane as alternative surface modification agent |
| |
| Authors: | Ha-Yoon Nah Vinayak G Parale Kyu-Yeon Lee Haryeong Choi Taehee Kim Chang-Hyun Lim Ji-Yeon Seo Yang Seo Ku Jae-Woo Park Hyung-Ho Park |
| |
| Institution: | 1.Department of Materials Science and Engineering,Yonsei University,Seoul,South Korea;2.Korea Institute of Ceramic Engineering and Technology,Jinju-si,South Korea;3.GLChem Co., Ltd.,Cheongju-si,South Korea |
| |
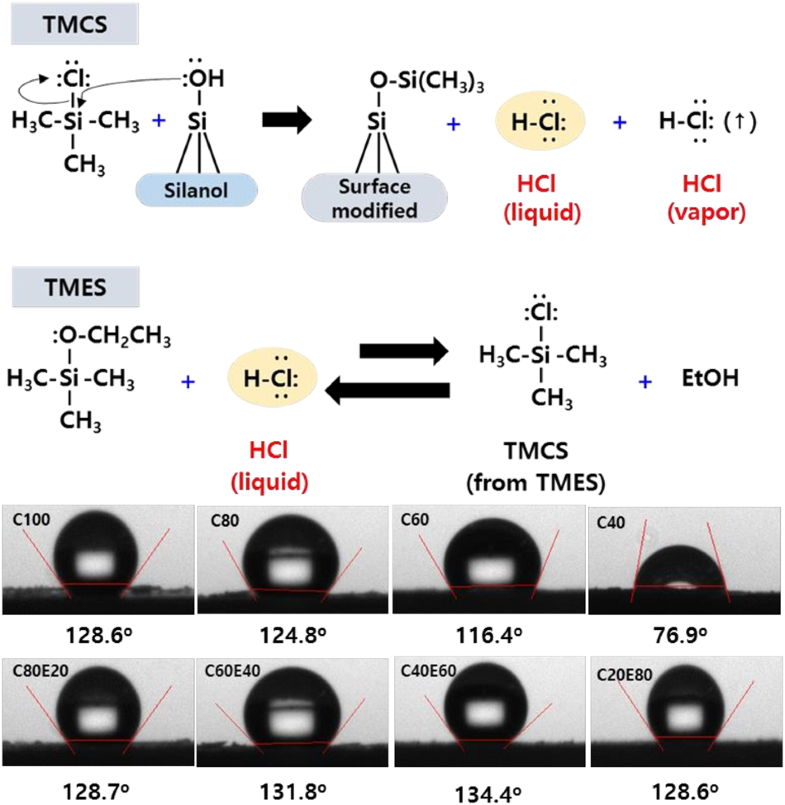
| Abstract: | Trimethylethoxysilane (TMES) has been recognized as a good co-precursor to increase the degree of hydrophobicity during the synthesis of a silica aerogel because of its methyl groups. Therefore, some physical properties of silica aerogels, including the contact angle and porosity, were investigated using TMES as a co-precursor at different molar ratios with the main precursor such as tetramethoxysilane (TMOS) or tetraethoxysilane (TEOS). In contrast to TMES, most silylating agents such as hexamethyldisilazane (HMDZ) and trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS) have been used for surface modification because of their ability to enhance the hydrophobicity of the aerogel surface. This work examines the silylation effect, which includes increasing hydrophobicity by TMES to determine the possibility of using it as an alternative silylating agent during ambient pressure drying in the synthesis of sodium silicate-based silica aerogel. In addition, the physical properties of sodium silicate-based silica aerogels with silylation under different TMES/TMCS volume ratio are investigated. The physical properties of sodium silicate-based aerogels can be changed by the TMES/TMCS volume ratio during the surface modification step. Aerogels with a high specific surface area (458?m2/g), pore volume (3.215?cm3/g), porosity (92.7%), and contact angle (131.8°) can be obtained TMES/TMCS volume ratio of 40/60. | |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 SpringerLink 等数据库收录! |
|