A Comparison of DESI-MS and LC-MS for the Lipidomic Profiling of Human Cancer Tissue |
| |
| Authors: | Nima Abbassi-Ghadi Emrys A. Jones Maria Gomez-Romero Ottmar Golf Sacheen Kumar Juzheng Huang Hiromi Kudo Rob D. Goldin George B. Hanna Zoltan Takats |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1.Department of Surgery and Cancer,Imperial College London,London,UK;2.Centre for Pathology,Imperial College London,London,UK |
| |
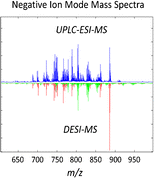
| Abstract: | In this study, we make a direct comparison between desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (DESI-MS) and ultraperformance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-MS) platforms for the profiling of glycerophospholipid (GPL) species in esophageal cancer tissue. In particular, we studied the similarities and differences in the range of GPLs detected and the congruency of their relative abundances as detected by each analytical platform. The main differences between mass spectra of the two modalities were found to be associated with the variance in adduct formation of common GPLs, rather than the presence of different GPL species. Phosphatidylcholines as formate adducts in UPLC-ESI-MS accounted for the majority of differences in negative ion mode and alkali metal adducts of phosphatidylcholines in DESI-MS for positive ion mode. Comparison of the relative abundance of GPLs, normalized to a common peak, revealed a correlation coefficient of 0.70 (P < 0.001). The GPL profile detected by DESI-MS is congruent to UPLC-ESI-MS, which reaffirms the role of DESI-MS for lipidomic profiling and a potential premise for quantification. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 SpringerLink 等数据库收录! |
|