|
|||||
|
|
Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers against the steroid testosterone |
|
| Authors: | |
| Institution: | 1.Interfibio, Nanobiotechnology & Bioanalysis Group, Departament d’Enginyeria Química,Universitat Rovira i Virgili,Tarragona,Spain;2.Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ),Tarragona,Spain;3.Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avan?ats (ICREA),Barcelona,Spain;4.Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,King Abdulaziz University,Jeddah,Saudi Arabia |
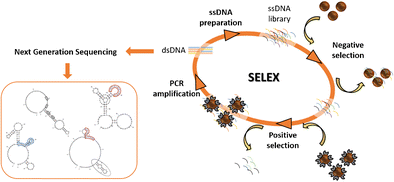
| Abstract: | Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) are frequently abused in human and animal sports as performance-enhancing drugs, and consequently their use is controlled by international sports authorities. Testosterone is one of the most frequently used AAS, and therefore the accurate determination of its levels in biological fluids is very important. The authors describe the selection of testosterone-binding aptamers performed using a classic SELEX approach with the target immobilized on magnetic beads. Counter selections with structurally similar steroids were implemented at different stages. Pools from different selection rounds were sequenced with Next Generation Sequencing and ten aptamer candidates were selected for further characterization. Low nanomolar range dissociation constants were calculated by a bead-based PCR assay and verified by microscale thermophoresis. Future work will focus on the development of aptamer-based platforms for the sensitive detection of testosterone in biological samples and the validation of these assays for the rapid screening of suspicious samples. Graphical abstract The selection of testosterone-binding aptamers is described via classic SELEX using the target immobilized on magnetic beads combined with Next Generation Sequencing. The process let to the identification of several unique aptamer candidates which were characterized and their binding to testosterone was evaluated. |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 SpringerLink 等数据库收录! | |