Participation of C-H Protons in the Dissociation of a Proton Deficient Dipeptide |
| |
| Authors: | Damodar Koirala Sabyasachy Mistry Paul G Wenthold |
| |
| Institution: | 1.Department of Chemistry,Purdue University,West Lafayette,USA |
| |
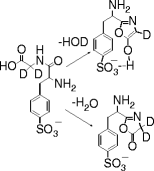
| Abstract: | The dissociation of anionic dipeptides Phe*Gly and GlyPhe*, where Phe* refers to sulfonated phenyl alanine, has been investigated by using ion trap mass spectrometry. The dipeptides undergo collision-induced dissociation (CID) to give the same products, indicating that they rearrange to a common structure before dissociation. The rearrangement does not occur with the dipeptide methyl esters. The structures of the b2 ions were investigated to determine the effect that having a remote, anionic site has on product formation. Comparison with the CID spectra for authentic structures shows that the b2 ion obtained from GlyPhe* has predominantly a diketopiperazine structure. The CID spectra for the Phe*Gly b2 ion and the authentic oxazolone are similar, but differences in intensity suggest a two-component mixture. Isotopic labeling studies are consistent with the formation of two products, with one resulting from loss of a non-mobile proton on the Gly α-carbon. The results are attributed to the formation of an oxazole and oxazolone enol product. Electronic structure calculations predict that the enol structure of the Phe*Gly b2 ion is lower in energy than the keto version due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding with the sulfonate group. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 SpringerLink 等数据库收录! |
|