A mini-review of the electro-peroxone technology for wastewaters: Characteristics,mechanism and prospect |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. College of Environment, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310032, China;2. College of Environmental and Resources Sciences, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou 311300, China;3. School of Biological and Chemical Engineering, NingboTech University, Ningbo 315100, China;1. College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, China;2. State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China |
| |
| Abstract: | 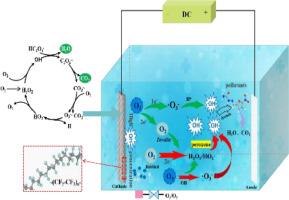
The electro-peroxone technology, a novel type of advanced oxidation technology, is widely used in wastewater treatment. Herein, this paper reviews the advantages and problems of the electro-peroxone technology compared with electrochemical oxidation technology, ozonation technology, and traditional peroxone technology. Due to the high kinetics of pollutant degradation, the electro-peroxone process can reduce the reaction time and energy consumption of pollutant treatment in wastewater. The electro-peroxone technology can promote pollutant degradation and mineralization, which shows obvious synergistic effects of electrochemical oxidation and ozonation for wastewater treatment. Most importantly, the research mechanism of the electro-peroxone technology is systematically introduced from two aspects of cathode reaction and bulk reaction. The influence of experimental parameters on the wastewater treatment effect is also discussed. Finally, the potential applications and future research directions of the electro-peroxone technology in the wastewater field are proposed. The electro-peroxone process can offer a highly efficient and energy saving water treatment method to improve the performance of existing ozonation and electrochemical systems and has therefore become a promising electrochemical advanced oxidation process for wastewater treatment. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

