Optical and electrical properties of copper-doped nano-crystallite CdO thin films |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Chemistry, Shahrood University of Technology, Shahrood, 36199-95161, Iran;2. Department of Chemistry, Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences, Gava Zang, Zanjan, 45137-66731, Iran;3. School of Pharmacy, Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, 1432-1 Horinouchi, Hachioji, Tokyo, 192-0392, Japan;1. Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital, Perth, Australia;2. Curtin University, School of Public Health, Australia;3. Fiona Stanley Hospital, Australia;4. Centre for Applied Statistics, University of Western Australia, Australia;5. St John of God Hospital, Subiaco, Western Australia 6009, Australia;6. Monash University, Australia;7. The Canberra Hospital, Australia;8. Australian National University Medical School, Australia;1. First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310006, China;2. Shanxi Hospital of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, Taiyuan, Shanxi 030000, China;1. Department of Physics, Sri Muthukumaran Institute of Technology, Chennai 600069, India;2. Department of Nuclear Physics, University of Madras, Chennai 600025, India;3. Electrochemical Materials Science Division, CSIR-Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi, 630006, India;1. Department of Physics, Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology, Hisar 125001, Haryana, India;2. Materials Research Laboratory, Department of Physics, Deenbandhu Chhotu Ram University of Science & Technology, Murthal 131039, Haryana, India |
| |
| Abstract: | 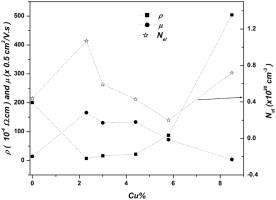
Thin films of Cu-doped CdO (CdO:Cu) with different Cu% content were prepared in high vacuum on glass and Si substrates. The samples were characterised X-ray diffraction (XRD), optical spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope (SEM), and dc-electrical measurements. The XRD study reveals the formation of single crystalline phase CdO:Cu of CdO structure with a preferential [111] orientation. However, with increasing of Cu% content, the crystal structure was gradually deteriorated. SEM study shows formation of granular structure with rice shape grains of average size ∼500 nm. The optical study shows that Cu doping increased the films transparency with a slight blueshift for the bandgap. The calculated optical constants for pure and Cu-doped CdO were analysed with Forouhi–Bloomer (FB), Wemple–Didomenico (WD), and Spitzer–Fan (SF) models. Good agreements were obtained between electrical and optical (through SF model) measurements. The electrical measurements show that the utmost enhancement in mobility (82.5 cm2/V s) and conductivity (1428.6 S/cm) was found with 2.3% Cu sample. The optoelectronic study was analysed through the available BGW and BGN models that show close theoretical to the experimental results. In general, the films of CdO prepared with light Cu doping have optical and electrical characteristics suitable for various applications in material sciences and optoelectronic devices. |
| |
| Keywords: | Cadmium–copper oxide Cu-doped CdO Doping TCO Optical properties |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

