Optical and dielectrical properties of azo quinoline thin films |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Organic & Inorganic Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, Urmia University, Urmia 57159, Iran;2. Department of Chemistry and Biotechnology, Swinburne University of Technology, Hawthorn VIC 3122, Australia;3. Centro de Química, Universidade do Minho, Campus de Gualtar, Braga 4710-057, Portugal;4. Centro de-Química- Vila Real, Universidade de Tràs-os-Montes e Alto Douro, Vila Real 5001-801, Portugal;5. School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University Malaysia, Jalan Sunsuria, Bandar Sunsuria, Sepang 43900, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia;6. Golestan Rheumatology Research Center, Golestan University of Medical Science, Gorgan, Iran |
| |
| Abstract: | 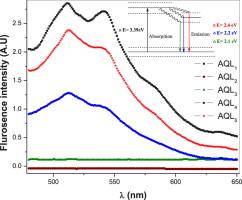
In this study, the optical and dielectrical properties of a novel series of quinoline azodyes (5-(4′-derivatives phenyl azo)-8-hydroxy-7-quinolinecarboxaldehyde) (AQL1–AQL5) were investigated and the obtained results were analyzed. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of AQLn show that the materials in the powder form are a mixture of amorphous and crystalline structure, while the thermally deposited thin films are completely amorphous. The optical constants such as the refractive index, n, the absorption index, k and the absorption coefficient, α, were determined using spectrophotometric measurements of transmittance (T) and reflectance (R) in the wavelength range 200–2500 nm. According to the single oscillator model (SOM), some related parameters such as oscillation energy (Eo), the dispersion energy (Ed), the optical dielectric constant (ε∞), the lattice dielectric constant (εL) and the ratio of free carrier concentration to its effective mass (N/m*) are estimated. The emission spectra of azo quinoline ligands (AQLn) exhibit dual fluorescence peaks in the region 512–580 nm. This finding reveals the formation of two stoichiometric hydrogen-bonding in the ground and excited state. The dielectrical properties and alternating current conductivity (σAC) are investigated in temperature range 298–483 K and frequency range 0.1–100 KHz. |
| |
| Keywords: | Quinoline azo compounds Thin films Optical properties Electrical conductivity |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

