Spatial Ion Peak Compression and its Utility in Ion Mobility Spectrometry |
| |
| Authors: | Sandilya V. B. Garimella Yehia M. Ibrahim Keqi Tang Ian K. Webb Erin S. Baker Aleksey V. Tolmachev Tsung-Chi Chen Gordon A. Anderson Richard D. Smith |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1.Biological Sciences Division,Pacific Northwest National Laboratory,Richland,USA |
| |
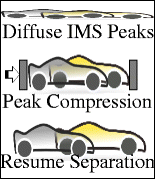
| Abstract: | A novel concept for ion spatial peak compression is described, and discussed primarily in the context of ion mobility spectrometry (IMS). Using theoretical and numerical methods, the effects of using non-constant (e.g., linearly varying) electric fields on ion distributions (e.g., an ion mobility peak) is evaluated both in the physical and temporal domains. The application of a linearly decreasing electric field in conjunction with conventional drift field arrangements is shown to lead to a reduction in IMS physical peak width. When multiple ion packets (i.e., peaks) in a selected mobility window are simultaneously subjected to such fields, there is ion packet compression (i.e., a reduction in peak widths for all species). This peak compression occurs with only a modest reduction of resolution, which can be quickly recovered as ions drift in a constant field after the compression event. Compression also yields a significant increase in peak intensities. Ion mobility peak compression can be particularly useful for mitigating diffusion-driven peak broadening over very long path length separations (e.g., in cyclic multi-pass arrangements), and for achieving higher S/N and IMS resolution over a selected mobility range. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 SpringerLink 等数据库收录! |
|