Synthesis modified structural and dielectric properties of semiconducting zinc ferrospinels |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry, Eastern European National University, 13 Voli Avenue, Lutsk 43025, Ukraine;2. Laboratory of Nanosciences Research (LNR), E.A. no 4682, UFR Sciences, University of Reims, 21 rue Clément Ader, 51685 Reims Cedex 02, France;3. Research Chair of Exploitation of Renewable Energy Applications in Saudi Arabia, Physics and Astronomy Department, College of Science, King Saud University, P.O. Box 2455, Riyadh 11451, Saudi Arabia;4. Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Abbassia, Cairo 11566, Egypt;5. Wireless and Photonic Networks Research Centre, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia;6. Institute of Physics, Czestochowa University of Technology, Armii Krajowej 13/15, PL-42-201 Czestochowa, Poland;7. Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czestochowa University Technology, Armii Krajowej 17, Pl-42-201 Czestochowa, Poland;8. Department of Inorganic and Organic Chemistry, Lviv National University of Veterinary Medicine and Biotechnologies, Pekarska St., 50, 79010 Lviv, Ukraine;9. Department of Physics and Mathematics, Lviv National University of Veterinary Medicine and Biotechnologies, Pekarska St., 50, 79010 Lviv, Ukraine;10. Department of Solid''s Spectroscopy, G. V. Kurdyumov Institute for Metal Physics of the National Academy of Science of Ukraine, Bulvar Akademika Vernadskogo, 36, Kiev 03680, Ukraine;1. School of Information Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, PR China;2. Department of Physics, College of Physics and Electrical Engineering, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou 510006, PR China;1. Department of Physics, Arab-American University, Jenin, West Bank, Palestinian Authority;2. Department of Basic Sciences and Humanities, College of Engineering, University of Dammam, Dammam, Saudi Arabia;3. Group of Physics, Faculty of Engineering, Atilim University, 06836 Ankara, Turkey;1. School of Quantitative Sciences, Universiti Utara Malaysia, 06010 Sintok, Kedah, Malaysia;2. COMSATS Institute of Information Technology, Attock 43600, Punjab, Pakistan;1. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Russia;2. Physics Research Laboratory, Voronezh Technical State University, Russia |
| |
| Abstract: | 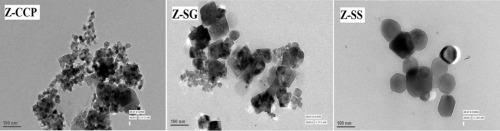
The influence of preparation techniques on structural and dielectric properties of ZnCrxFe1−xO4 (x=0, 0.1 abbreviated as Z and ZC) ferrite nano-particles synthesized using chemical co-precipitation (CCP), sol-gel (SG) and solid state reaction (SS) techniques is discussed. XRD profiles are used to confirm the single phase spinel ferrite formation. TEM images indicate the change in size and shape of particles on changing either the composition or the synthesis methodology. The TEM micrograph of samples obtained through CCP shows uniform particle size formation compared to those obtained through SG and SS. Sample prepared through CCP possess porosity >70% making these materials suitable for sensing applications. The dielectric loss, dielectric constant and ac conductivity are analyzed as a function of frequency, temperature and composition using impedance spectroscopy. A universal dielectric behavior has been predicted through temperature and frequency variations of different parameters. Dielectric constant is found to possess highest value for sample synthesized through SG which marks the possibility of using the SG derived ferrospinels as microwave device components. |
| |
| Keywords: | Magnetic materials Chemical synthesis Impedance spectroscopy Dielectric properties |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

