| 激光惯性约束聚变中光学汤姆逊散射研究进展 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 李志超, 赵航, 龚韬, 等. 激光惯性约束聚变中光学汤姆逊散射研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32: 092004. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200130 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 李志超 赵航 龚韬 李欣 杨冬 蒋小华 郑坚 刘永刚 刘耀远 陈朝鑫 李三伟 李琦 潘凯强 郭亮 理玉龙 徐涛 彭晓世 吴畅书 张桦森 郝亮 蓝可 陈耀桦 郑春阳 古培俊 王峰 蔡洪波 郑无敌 邹士阳 杨家敏 江少恩 张保汉 朱少平 丁永坤 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心,四川 绵阳 621900;;2.北京应用物理与计算数学研究所,北京 100088;;3.中国科学技术大学 工程与应用物理系,合肥 230026 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFA0403300);科学挑战专题项目(TZ2016005);国家自然科学基金项目(11975215,11905204,11875241,11705180) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 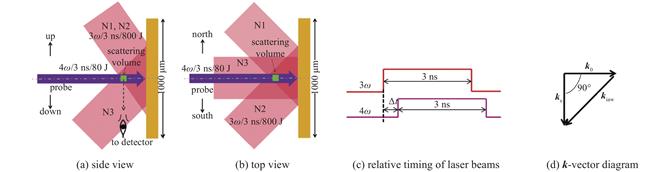
当前,激光惯性约束聚变在越来越接近点火的极端能量密度条件下,实验与模拟的偏离逐渐增大,一个关键原因是缺乏对黑腔等离子体状态及其影响黑腔能量学和内爆对称性的细致研究和判断。光学汤姆逊散射主动式、诊断精确、参数完备的优点,使之成为激光惯性约束聚变黑腔等离子体状态参数精密诊断的标准方法。中国面向激光惯性约束聚变研究的光学汤姆逊散射实验技术的发展与神光系列激光装置的建设和在其上开展的物理实验紧密相关。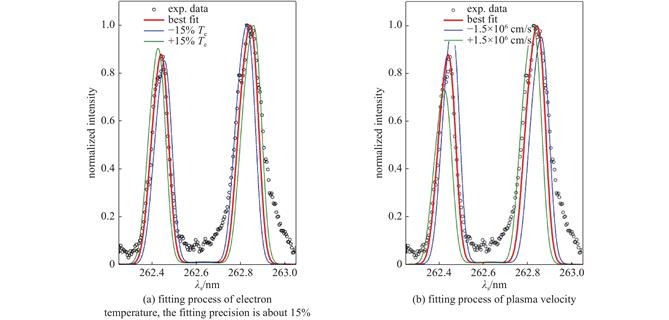
近年来,四倍频汤姆逊散射实验技术在神光III原型和100 kJ激光装置上相继建立,部分实验结果不仅加深了对激光惯性约束聚变靶物理的认识,还反映了实验条件对汤姆逊散射诊断的影响,促进了实验技术的精密化发展。在未来,还需要进一步发展多支路汤姆逊散射、五倍频汤姆逊散射和超热相干汤姆逊散射等新技术,面向点火黑腔条件,大幅提升激光等离子体状态参数的诊断精度,开展新物理机制的探索和研究,在激光惯性约束聚变和其他高能量密度物理科学领域发挥更重要的作用。

|
| 关 键 词: | 激光惯性约束聚变 光学汤姆逊散射 等离子体状态参数 激光等离子体不稳定性 |
| 收稿时间: | 2020-05-17 |
| 修稿时间: | 2020-07-12 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《强激光与粒子束》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《强激光与粒子束》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



