
|
|||||
|
|
Dielectric relaxation of PrFeO3 nanoparticles |
|
| Affiliation: | 1. Grupo de Transiciones de Fase y materiales funcionales, Departamento de Física, Universidad del Valle, Santiago de Cali, Colombia;2. CYTEMAC, Departamento de Física, Universidad del Cauca, Popayán, Colombia;3. Centro de Excelencia en Nuevos Materiales (CENM), Universidad del Valle, Santiago de Cali, Colombia;4. Departamento de Ingeniería Química, Biotecnología y Materiales, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile |
| Abstract: | 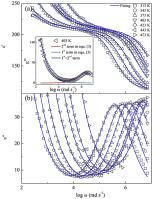 PrFeO3 (PFO) nanoceramic is synthesized by a sol-gel reaction technique. Thermogravimetric study of the as prepared gel is performed to get the lowest possible calcination temperature of PFO nanoparticles. The Rietveld refinement of the powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern shows that the sample crystallizes in the orthorhombic (Pnma) phase at room temperature. The particle size of the sample is determined by scanning electron microscopy. The vibrational properties of the samples are studied by Raman spectroscopy at an excitation wavelength of 488 nm to substantiate the XRD results. Group-theoretical study is performed to assign the different vibrational modes of the sample in accordance with structural symmetry. Dielectric spectroscopy is applied to investigate the ac electrical properties of PFO at various temperatures between 313 and 473 K and in a frequency range of 42 Hz–1.1 MHz. The modified Cole-Cole equation is used to describe the experimental dielectric spectra. The frequency-dependent conductivity spectra are found to follow the power law. The temperature dependent dc conductivity is found to obey the Arrhenius law with an activation energy of 0.280 eV. An analysis of the real and imaginary parts of impedance is performed, assuming a distribution of relaxation times as confirmed by Cole-Cole plot. |
| Keywords: | Nanoparticles Rietveld refinement Raman spectroscopy Cole-Cole equation Activation energy |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! | |