Defect formation and magnetic properties of carbon-doped ZnO nanowires by the first principles |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Institute of Problems of Material Science, National Academy of Science of Ukraine, Krzhyzhanosky str. 3, 03142 Kyiv, Ukraine;2. Department of Chemistry, Technical University Munich, Lichtenbergstrasse 4, D-85747 Garching, Germany;3. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (L-352), P.O. Box 808, Livermore, CA 94551, USA;4. Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Interdisciplinary Center for Nanotoxicity, Jackson State University, Jackson, MS 39217, USA;5. U.S. Army ERDC, Vicksburg, MS 39180, USA |
| |
| Abstract: | 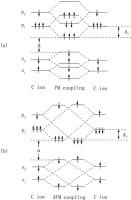
Theoretical calculation based on density functional theory (DFT) and local density approximation (LDA) with Hubbard parameters has been carried out in studying defect formation energy, transition energy and ferromagnetism of carbon-doped ZnO nanowires (NW). The formation and ionization characteristics of the defects [CO (B), CO (S), CZn (B), VO (B), VZn (B), IO (oct) and IZn (oct)] in ZnO NW are analyzed in the text. Ferromagnetic (FM) and antiferromagnetic (AFM) coupling between C atoms are also investigated by 9 different configurations. The FM and AFM stability are explained by the interaction of C energy level. In addition, the vacancies [VO (B) and VZn (B)] and interstitials [IO (oct) and IZn (oct)] affecting the FM coupling are also investigated. It is found that magnetic moment of C 2p can be mediated by these defects. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

