Electrochemical detection of perchloroethylene using differential pulse voltammetry |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, PR China;2. North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou 450045, PR China |
| |
| Abstract: | 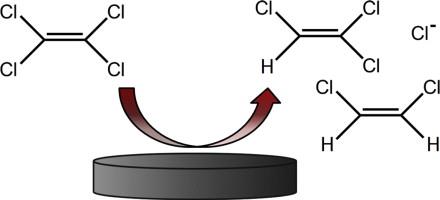
We demonstrate the application of differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) for the electrochemical detection of perchloroethylene (PCE) on an unmodified glassy carbon electrode surface. Detection sensitivity was substantially improved using DPV, in which dechlorination was denoted by a cathodic peak observed at approximately − 0.6 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Peak current intensity was found to correlate linearly with concentration over a tested range of 0 to 10 μM. The utility of this technique was subsequently evaluated for PCE-spiked environmental samples containing either Methylobacterium adhaesivum (1 × 106 cells/mL) or creek water (10% v/v). In all environmental samples, a linear dynamic range was also observed from approximately 0 to 10 μM. The limit of detection was determined to be 0.3 μM in blank buffer, 0.4 μM in bacteria-containing samples and 1.2 μM in creek water samples. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

