化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (4): 510-516.DOI: 10.6023/A21110533 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
龚雪a, 马新国a,b,*( ), 万锋达a, 段汪洋a, 杨小玲a,b, 朱进容a,b
), 万锋达a, 段汪洋a, 杨小玲a,b, 朱进容a,b
投稿日期:2021-11-24
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
马新国
基金资助:
Xue Gonga, Xinguo Maa,b( ), Fengda Wana, Wangyang Duana, Xiaoling Yanga,b, Jinrong Zhua,b
), Fengda Wana, Wangyang Duana, Xiaoling Yanga,b, Jinrong Zhua,b
Received:2021-11-24
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
Xinguo Ma
Supported by:文章分享

采用平面波超软赝势方法研究了二维单层MoSi2X4 (X=N, P, As)的稳定性、电子结构和光学性质. 研究结果显示, 基于单层MoSi2N4的两种同分异构体M1和M2所构建的六种晶体结构具有较好的动力学稳定性. 通过能带和有效质量的计算, 单层MoSi2N4在MoSi2X4 (X=N, P, As)六种晶体结构中显示出最宽的间接带隙和最高的载流子迁移率. 随后带边电位的计算结果表明, 单层MoSi2N4带边势分别为M1: –0.368、1.416 V, M2: –0.227、1.837 V, 其结果相较于MoSi2P4和MoSi2As4导带边电位更负, 价带边电位更正, 是六种晶体结构中最适合用作光催化剂的材料. 同时, 光吸收谱的计算结果显示, 单层MoSi2N4的光学吸收表现出明显的各向异性, 在可见光和紫外光波段内具有较强的光吸收能力, 说明其在可见光催化领域有着潜在的应用前景. 这些结果为进一步深入研究二维单层MoSi2N4在光催化水解领域的应用提供了理论指导.
龚雪, 马新国, 万锋达, 段汪洋, 杨小玲, 朱进容. 二维单层MoSi2X4 (X=N, P, As)的电子结构及光学性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 510-516.
Xue Gong, Xinguo Ma, Fengda Wan, Wangyang Duan, Xiaoling Yang, Jinrong Zhu. Study on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Two-dimensional Monolayer MoSi2X4 (X=N, P, As)[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 510-516.
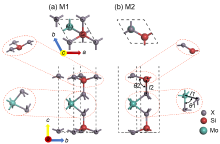
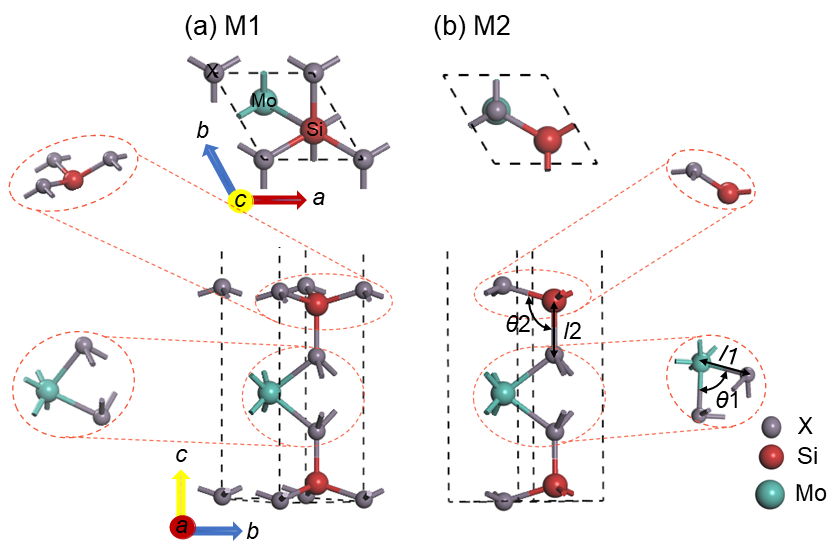
| Structure | Model | a/nm | b/nm | Eg/eV | Bond length/nm | Bond angle/(°) | Cohesive energy/(eV•atom–1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l1 | l2 | θ1 | θ2 | |||||||
| MoSi2N4 | M1 | 0.290 | 0.290 | 1.783 | 0.209 | 0.175 | 73.36 | 106.61 | –5.29 | |
| 0.175 | ||||||||||
| M2 | 0.289 | 0.289 | 2.064 | 0.209 | 0.175 | 74.08 | 107.01 | –5.28 | ||
| 0.175 | ||||||||||
| MoSi2P4 | M1 | 0.347 | 0.347 | 0.657 | 0.245 | 0.224 | 70.44 | 116.96 | –3.30 | |
| 0.225 | ||||||||||
| M2 | 0.346 | 0.346 | 0.889 | 0.245 | 0.226 | 70.99 | 117.34 | –3.29 | ||
| 0.225 | ||||||||||
| MoSi2As4 | M1 | 0.365 | 0.366 | 0.559 | 0.257 | 0.236 | 69.97 | 117.94 | –2.94 | |
| 0.237 | ||||||||||
| M2 | 0.364 | 0.365 | 0.709 | 0.257 | 0.240 | 70.26 | 116.85 | –2.93 | ||
| 0.238 | ||||||||||
| Structure | Model | a/nm | b/nm | Eg/eV | Bond length/nm | Bond angle/(°) | Cohesive energy/(eV•atom–1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l1 | l2 | θ1 | θ2 | |||||||
| MoSi2N4 | M1 | 0.290 | 0.290 | 1.783 | 0.209 | 0.175 | 73.36 | 106.61 | –5.29 | |
| 0.175 | ||||||||||
| M2 | 0.289 | 0.289 | 2.064 | 0.209 | 0.175 | 74.08 | 107.01 | –5.28 | ||
| 0.175 | ||||||||||
| MoSi2P4 | M1 | 0.347 | 0.347 | 0.657 | 0.245 | 0.224 | 70.44 | 116.96 | –3.30 | |
| 0.225 | ||||||||||
| M2 | 0.346 | 0.346 | 0.889 | 0.245 | 0.226 | 70.99 | 117.34 | –3.29 | ||
| 0.225 | ||||||||||
| MoSi2As4 | M1 | 0.365 | 0.366 | 0.559 | 0.257 | 0.236 | 69.97 | 117.94 | –2.94 | |
| 0.237 | ||||||||||
| M2 | 0.364 | 0.365 | 0.709 | 0.257 | 0.240 | 70.26 | 116.85 | –2.93 | ||
| 0.238 | ||||||||||
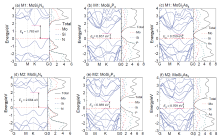

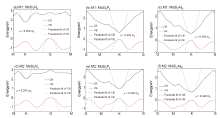
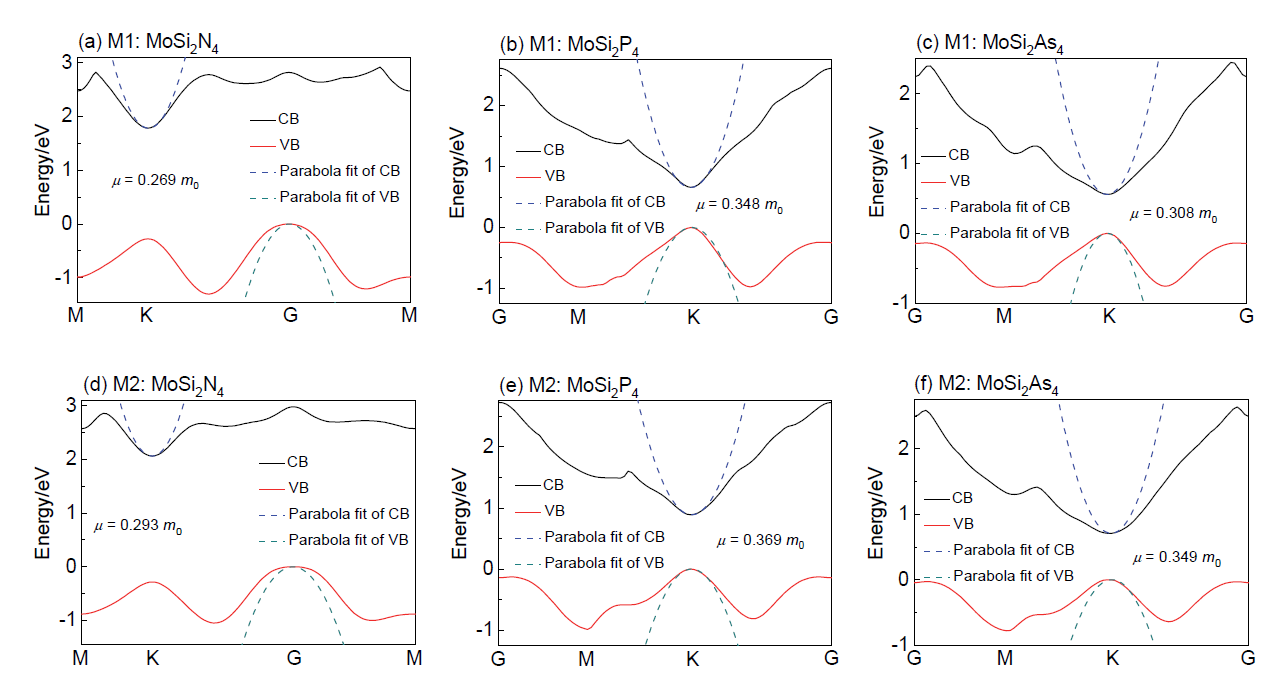
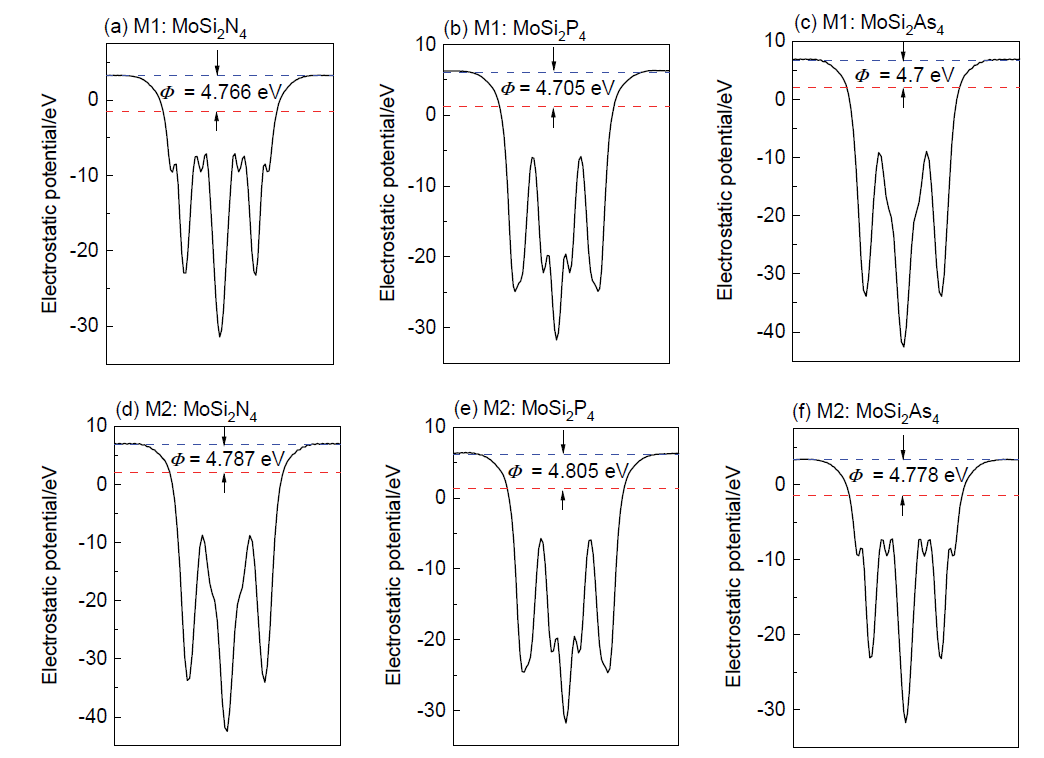
| Structure | Model | $m_{e}^{*}$/m0 | $m_{h}^{*}$/m0 | μ0/m0 | Work function/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoSi2N4 | M1 | 0.461 | 0.644 | 0.269 | 4.766 |
| M2 | 0.462 | 0.798 | 0.293 | 4.787 | |
| MoSi2P4 | M1 | 0.615 | 0.799 | 0.348 | 4.705 |
| M2 | 0.702 | 0.778 | 0.369 | 4.805 | |
| MoSi2As4 | M1 | 0.625 | 0.606 | 0.308 | 4.700 |
| M2 | 0.614 | 0.806 | 0.349 | 4.778 | |
| MoS2 | 0.457 | 0.779 | 0.288 | 5.149 |
| Structure | Model | $m_{e}^{*}$/m0 | $m_{h}^{*}$/m0 | μ0/m0 | Work function/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoSi2N4 | M1 | 0.461 | 0.644 | 0.269 | 4.766 |
| M2 | 0.462 | 0.798 | 0.293 | 4.787 | |
| MoSi2P4 | M1 | 0.615 | 0.799 | 0.348 | 4.705 |
| M2 | 0.702 | 0.778 | 0.369 | 4.805 | |
| MoSi2As4 | M1 | 0.625 | 0.606 | 0.308 | 4.700 |
| M2 | 0.614 | 0.806 | 0.349 | 4.778 | |
| MoS2 | 0.457 | 0.779 | 0.288 | 5.149 |
| [1] |
Muñoz, V.; Casado, C.; Suárez, S.; Sánchez, B.; Marugán, J. Catal. Today 2019, 326, 82.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.09.001 |
| [2] |
Mo, J. H.; Zhang, Y. P.; Xu, Q. J.; Lamson, J. J.; Zhao, R. Y. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2229.
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.01.034 |
| [3] |
Wang, S. B.; Ang, H. M.; Tade, M. O. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 694.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.02.011 |
| [4] |
Chen, Q.; Kuang, Q.; Xie, Z. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 10. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20080384 |
|
(陈钱, 匡勤, 谢兆雄, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 10.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080384 |
|
| [5] |
Wang, R. Z.; Zou, Y. J.; Hong, S.; Xu, M. K.; Ling, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 932. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21030118 |
|
(王瑞兆, 邹云杰, 洪晟, 徐铭楷, 凌岚, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 932.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030118 |
|
| [6] |
Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D. A.; Dommett, G. H. B.; Kohlhaas, K. M.; Zimney, E. J.; Stach, E. A.; Piner, R. D.; Nguyen, S. T.; Ruoff, R. S. Nature 2006, 442, 282.
doi: 10.1038/nature04969 |
| [7] |
Liu, H.; Li, J. Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, G. Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, L. F.; Qi, H.; Duo, S. W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1293. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21060265 |
|
(刘欢, 李京哲, 李平, 张广智, 徐迅, 张豪, 邱灵芳, 齐晖, 多树旺, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1293.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060265 |
|
| [8] |
Karlicky, F.; Kasibhatta, K. R. D.; Otyepka, M.; Zboril, R. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6434.
doi: 10.1021/nn4024027 |
| [9] |
Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K.; Morozov, S. V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S. V.; Grigorieva, I. V.; Firsov, A. A. Science 2004, 306, 666.
pmid: 15499015 |
| [10] |
Novoselov, K. S.; Falko, V. I.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P. R.; Schwab, M. G.; Kim, K. Nature 2012, 490, 192.
doi: 10.1038/nature11458 |
| [11] |
Kim, K. S.; Zhao, Y.; Jang, H.; Lee, S. Y.; Kim, J. M.; Kim, K. S.; Ahn, J. H.; Kim, P.; Choi, J. Y.; Hong, B. H. Nature 2009, 457, 706.
doi: 10.1038/nature07719 |
| [12] |
Balandin, A. A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C. N. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902.
doi: 10.1021/nl0731872 |
| [13] |
Niu, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Cheng, H. M. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4763.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201200922 |
| [14] |
Zhou, L.; Xia, T. Y.; Cao, T. Q.; Wang, L. R.; Chen, Y. S.; Li, S. F.; Wang, R. M.; Guo, H. Z. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 818, 152909.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152909 |
| [15] |
Ye, G. L.; Gong, Y. J.; Lin, J. H.; Li, B.; He, Y. M.; Pantelides, S. T.; Zhou, W.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P. M. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1097.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04331 |
| [16] |
Zong, X.; Yan, H. J.; Wu, G. P.; Ma, G. J.; Wen, F. Y.; Wang, L.; Li, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7176.
doi: 10.1021/ja8007825 pmid: 18473462 |
| [17] |
Laursen, A. B.; Kegnæs, S.; Dahla, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5577.
doi: 10.1039/c2ee02618j |
| [18] |
Li, Y. G.; Li, Y. L.; Araujo, C. M.; Luo, W.; Ahuja, R. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2214.
doi: 10.1039/c3cy00207a |
| [19] |
Quinn, M. D. J.; Ho, N. H.; Notley, S. M. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12751.
doi: 10.1021/am404161k |
| [20] |
Hong, Y. L.; Liu, Z. B.; Wang, L.; Zhou, T. Y.; Ma, W.; Xu, C.; Feng, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, M. L.; Sun, D. M.; Chen, X. Q.; Cheng, H. M.; Ren, W. C. Science 2020, 369, 670.
doi: 10.1126/science.abb7023 |
| [21] |
Bafekry, A.; Faraji, M.; Hoat, D. M.; Fadlallab, M. M.; Shahrokhi, M.; Shojaei, F.; Gogova, D.; Ghergherehchi, M. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 155303.
doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/abdb6b |
| [22] |
Novoselov, K. S.; Ge, Q.; Daria, V. A. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 559.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz202 pmid: 34692074 |
| [23] |
Li, Q. F.; Zhou, W. X.; Wan, X. G.; Zhou, J. Phys. E (Amsterdam, Neth.) 2021, 131, 114753.
|
| [24] |
Yu, J. H.; Zhou, J.; Wan, X. G.; Li, Q. F. New J. Phys. 2021, 23, 033005.
doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/abe8f7 |
| [25] |
Cai, Y. Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6269.
doi: 10.1021/ja4109787 |
| [26] |
Vanderbilt, D. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.41.7892 |
| [27] |
Kohn, W.; Sham, L. J. J. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, 1133.
|
| [28] |
Monkhorst, H. J.; Pack, J. D. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.13.5188 |
| [29] |
Segall, M. D.; Lindan, P. J. D.; Probert, M. J.; Pickard, C. J.; Hasnip, P. J.; Clark, S. J.; Payne, M. C. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2717.
|
| [30] |
Wang, H. Y. Ph.D. Dissertation, Zhongnan University, Changsha, 2008. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王焕友, 博士论文, 中南大学, 长沙, 2008.)
|
|
| [31] |
Yu, W. L.; Zhang, J. F.; Peng, T. Y. Appl. Catal., B 2016, 181, 220.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.031 |
| [32] |
Ma, X. G.; Lu, B.; Li, D.; Shi, R.; Pan, C. S.; Zhu, Y. F. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4680.
doi: 10.1021/jp111167u |
| [33] |
Garg, R.; Dutta, N. K.; Choudhury, N. R. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 267.
doi: 10.3390/nano4020267 |
| [34] |
Xu, Y.; Schoonen, M. A. A. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 543.
doi: 10.2138/am-2000-0416 |
| [35] |
Chun, W. J.; Ishikawa, A.; Fujisawa, H.; Takata, T.; Kondo, J. N.; Hara, M.; Kawai, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Domen, K. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 1798.
doi: 10.1021/jp027593f |
| [36] |
Hong, Y. L. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 2020. (in Chinese)
|
|
(洪艺伦, 博士论文, 中国科学技术大学, 合肥, 2020.)
|
|
| [37] |
Peng, Q.; Wang, Z. Y.; Sa, B. S.; Wu, B.; Sun, Z. M. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31994.
doi: 10.1038/srep31994 |
| [1] | 陈健强, 朱钢国, 吴劼. 镍催化氮杂环丙烷的开环偶联反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 190-212. |
| [2] | 吴宇晗, 张栋栋, 尹宏宇, 陈正男, 赵文, 匙玉华. “双碳”目标下Janus In2S2X光催化还原CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1148-1156. |
| [3] | 张凯, 武晓君. 具有室温铁磁性的二维Janus钛硫属化物★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1142-1147. |
| [4] | 梁雪峰, 荆剑, 冯昕, 赵勇泽, 唐新员, 何燕, 张立胜, 李慧芳. 共价有机框架COF66/COF366的电子结构: 从单体到二维平面聚合物[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 717-724. |
| [5] | 何明慧, 叶子秋, 林桂庆, 尹晟, 黄心翊, 周旭, 尹颖, 桂波, 汪成. 卟啉基共价有机框架的光催化研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 784-792. |
| [6] | 刘嘉文, 林玮璜, 王惟嘉, 郭学益, 杨英. Cu1.94S-SnS纳米异质结的合成及其光催化降解研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 725-734. |
| [7] | 刘坜, 郑刚, 范国强, 杜洪光, 谭嘉靖. 4-酰基/氨基羰基/烷氧羰基取代汉斯酯参与的有机反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 657-668. |
| [8] | 李飞, 丁汇丽, 李超忠. 基于氟仿衍生的三氟甲基硼络合物参与的烯烃氢三氟甲基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 577-581. |
| [9] | 徐袁利, 潘辉, 杨义, 左智伟. 连续流条件下蒽-铈协同催化的苄位碳氢键选择性氧化反应★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 435-440. |
| [10] | 齐学平, 王飞, 张健. 后合成法构筑钛基金属有机框架及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 548-558. |
| [11] | 赵政嘉, 刘康, 郭燕, 于吉攀, 石伟群. 超铀金属有机化学研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1633-1641. |
| [12] | 陈健强, 朱钢国, 吴劼. 草酸酯类化合物在自由基脱羟基化反应中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1609-1623. |
| [13] | 郑冰, 王喆, 何静, 张姣, 戚文博, 张梦圆, 于海涛. 碱(土)金属/双层α-硼烯纳米复合体的结构和功函性质的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1357-1370. |
| [14] | 杨春晖, 陈景超, 李新汉, 孟丽, 王凯民, 孙蔚青, 樊保敏. 可见光催化的硅烷二氟烯丙基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 1-5. |
| [15] | 解众舒, 薛中鑫, 许子文, 李倩, 王洪宇, 李维实. 石墨相氮化碳的共轭交联修饰及其对可见光催化产氢性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1231-1237. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||